An intercooler is a critical component in turbocharged and supercharged engines. It cools the compressed air that is forced into the engine. This cooling process increases the air density, providing more oxygen for combustion, which improves engine power and efficiency. The compressed air heats up when compressed by a turbocharger or supercharger, decreasing its density and the oxygen content. An intercooler helps dissipate this heat, allowing the engine to receive cool, dense air, crucial for optimal performance.
The Science Behind Intercoolers
Oxygen plays a crucial role in the combustion process. For fuel to burn completely, the engine must receive a sufficient amount of air, particularly denser (cool) air. From basic science, we know:
- Cool air is denser than hot air, meaning it contains a higher concentration of oxygen.
- Adequate oxygen supply is essential for complete fuel combustion, maximizing engine power and efficiency while reducing waste and emissions.
An intercooler functions as a heat exchanger, cooling the hot compressed air to ensure better combustion.
From school education we all know that:
Cool air is denser, which means it has greater concentration of Oxygen as compared to hot air. The ability of the engine to burn the fuel completely, increases with the amount of oxygen supplied to the combustion chamber.
However, if limited amount of oxygen is available in the chamber at the time of combustion, then it is obvious that all the fuel won’t be burnt. The unburnt fuel is considered a waste and consequently with improper burning we will lose power and it will also contribute towards environmental emissions. Therefore, we need to provide sufficient quantity of oxygen to the engine for proper burning and eventually for better performance from the engine. The intercooler is a heat exchanger which cools the hot air and provide engine with cool dense air so that we can have better combustion.
How Does an Intercooler Work?
An intercooler is typically positioned between the turbo or supercharger and the engine, connected to the intake system. The compressed air flows through the intercooler, where it is cooled by the surrounding air. The intercooler is often made from aluminum or other heat-conductive materials, aiding in heat dissipation.
The process involves the following steps:
- Compression: Air is compressed by the turbocharger or supercharger, heating it up.
- Cooling: The hot compressed air passes through the intercooler, where it is cooled by ambient air or water, depending on the type of intercooler.
- Increased Density: As the air cools, its density increases, providing more oxygen for the combustion process.
- Enhanced Combustion: The cooled, dense air enters the engine's intake manifold, leading to better combustion, improved power output, and increased efficiency.
The air after it is cooled is fed to the intake manifold of the engine. Many turbocharged vehicles use air-to-air intercoolers, because due to their simplicity, light weight, and low price.
Types of Intercoolers
Air-to-Air Intercooler
An air-to-air intercooler uses ambient air to cool the compressed air. This type is the most common due to its simplicity, light weight, and cost-effectiveness. It works similarly to a radiator, directing compressed air past cooling fins and tiny tubes that absorb heat. The heat is then dissipated by the external air. Air-to-air intercoolers are widely used in many turbocharged vehicles.
Air-to-Water Intercooler
An air-to-water intercooler uses water to cool the compressed air. Cool water is pumped through the unit, absorbing heat from the air. Afterward, this heated water needs to be cooled, typically passing through a radiator or cooling circuit. For even better cooling, water can be replaced with a coolant. Air-to-water intercoolers are more efficient in heat transfer but are more complex, heavier, and costly, making them less popular for regular vehicles.
Benefits of Using an Intercooler
- Improved Engine Performance: By providing cool, dense air, an intercooler enhances the combustion process, leading to increased power and efficiency.
- Reduced Engine Knock: Cooler air helps to reduce the risk of engine knock, which can damage the engine.
- Lower Emissions: More efficient combustion results in fewer unburnt hydrocarbons, reducing harmful emissions.
- Enhanced Fuel Efficiency: With better combustion, the engine uses fuel more efficiently, improving overall fuel economy.
Maintenance Tips for Intercoolers
To keep an intercooler in good working condition, regular maintenance is essential:
- Cleaning: Periodically clean the intercooler to remove any debris or buildup that could obstruct airflow.
- Inspection: Regularly inspect the intercooler for any signs of damage or leaks.
- Coolant Levels: For air-to-water intercoolers, ensure that coolant levels are maintained, and the coolant is replaced as needed.
- Performance Checks: Monitor the performance of the intercooler and the engine, looking for any signs of reduced efficiency or power loss.
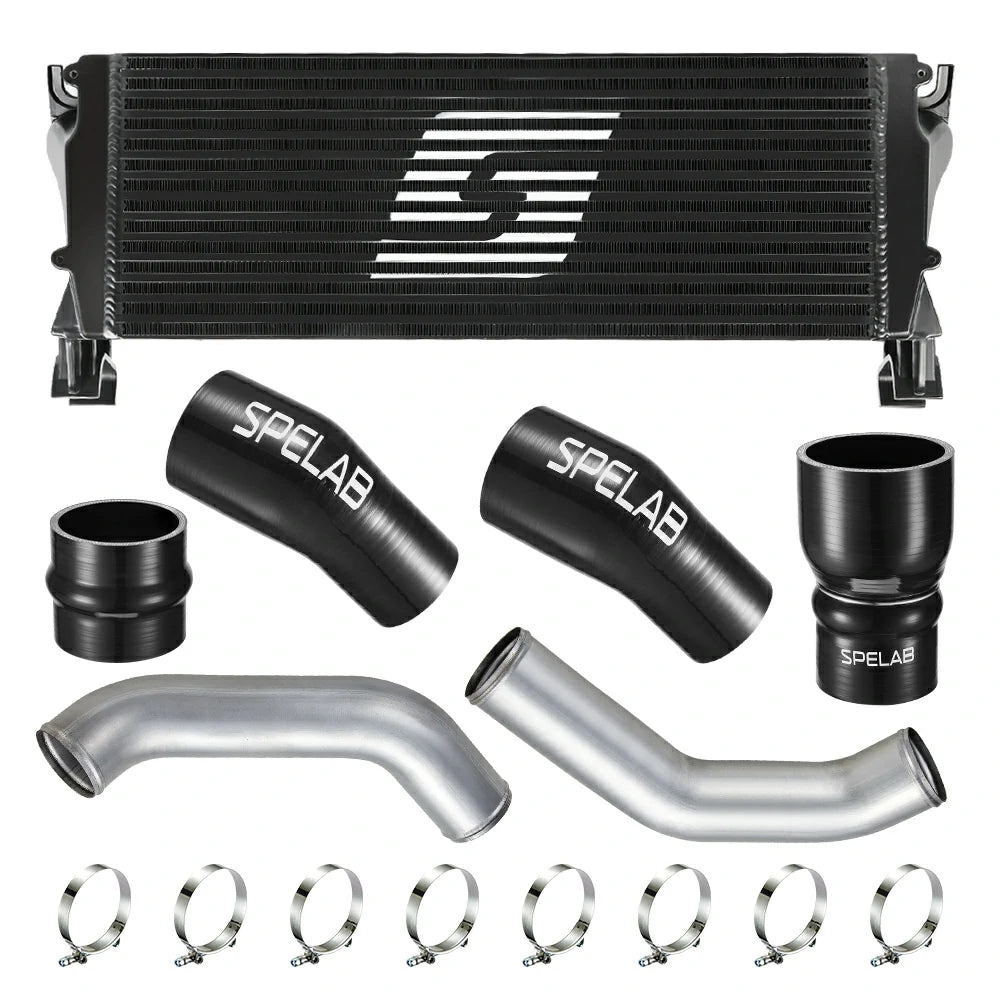

SPELAB Intercooler Kit for 2013-2018 6.7 Cummins Diesel Dodge
Performance Intercooler + Aluminized carbon steel Pipe
Buy NowConclusion
An intercooler is vital for turbocharged and supercharged engines because it increases the air density entering the engine, resulting in more oxygen for combustion. This leads to greater power and efficiency and reduces emissions. However, intercoolers can be damaged by high temperatures, so regular maintenance, such as cleaning and inspection, is essential to ensure optimal performance.
Understanding the workings and benefits of intercoolers can help you maintain your vehicle better and make informed decisions about upgrades and modifications. Whether you opt for an air-to-air or air-to-water intercooler, the goal remains the same: enhancing engine performance through effective cooling of compressed air.
FAQs
Q1: What is the function of an intercooler?
A1: The primary function of an intercooler is to cool the compressed air from the turbocharger or supercharger before it enters the engine. This cooling process increases the air density, providing more oxygen for combustion, which improves engine performance and efficiency.
Q2: How does an intercooler system work?
A2: An intercooler system works by passing hot, compressed air through a series of cooling fins or tubes. The heat is dissipated either by ambient air (air-to-air intercooler) or by water (air-to-water intercooler), resulting in cooler, denser air entering the engine.
Q3: Does an intercooler add horsepower?
A3: Yes, an intercooler can add horsepower by increasing the efficiency of the engine. By cooling the compressed air, it allows more oxygen to enter the combustion chamber, leading to more powerful and efficient combustion.
Q4: Does an intercooler have coolant in it?
A4: Some intercoolers, specifically air-to-water intercoolers, use coolant to help cool the compressed air. The coolant absorbs heat from the air and is then cooled itself, often through a radiator or cooling circuit.
Q5: Why do turbocharged engines use intercoolers?
A5: Turbocharged engines use intercoolers to cool the compressed air coming from the turbocharger. This cooling is essential to increase air density, improve combustion efficiency, reduce the risk of engine knock, and ultimately enhance engine performance.
Q6: What causes an intercooler to fail?
A6: Intercoolers can fail due to several reasons, including physical damage from debris, internal corrosion, leaks in the cooling fins or tubes, and excessive heat that can degrade materials over time. Regular maintenance and inspections can help prevent these issues.
Q7: What is the difference between air-to-air and air-to-water intercoolers?
A7: Air-to-air intercoolers use ambient air to cool the compressed air, while air-to-water intercoolers use water to achieve the same effect. Air-to-air intercoolers are simpler, lighter, and less expensive, whereas air-to-water intercoolers offer better cooling efficiency but are more complex and costly.
Q8: How does a turbocharger increase engine performance?
A8: A turbocharger increases engine performance by compressing the intake air, allowing more air to enter the combustion chamber. This increased air volume, combined with more fuel, leads to a more powerful combustion process and thus greater engine power.
Q9: What maintenance does an intercooler require?
A9: Intercooler maintenance includes regular cleaning to remove debris, inspecting for leaks or damage, ensuring coolant levels are adequate (for air-to-water intercoolers), and monitoring performance to detect any issues early.
Q10: Can an intercooler improve fuel efficiency?
A10: Yes, an intercooler can improve fuel efficiency by ensuring that the engine receives cool, dense air, which enhances the combustion process. Better combustion leads to more efficient fuel use and can reduce overall fuel consumption.