Explore EGR systems, their delete options, and maintenance tips. Learn how to optimize engine performance and emissions control effectively in this comprehensive guide.
1. History and Evolution of EGR Systems
The evolution of emissions control systems in automotive engineering has been pivotal in addressing environmental concerns while enhancing engine efficiency. Among these innovations, the Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) system stands out for its role in reducing nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions.
1.1 Introduction of Catalytic Converters
Catalytic converters marked a significant milestone in emissions control during the late 20th century. These devices primarily targeted carbon monoxide (CO) and hydrocarbon (HC) emissions, laying the groundwork for more advanced systems like EGR.
1.2 Emergence of Early EGR Systems
Early EGR systems were introduced in response to tightening emissions regulations in the 1970s. They aimed to recirculate a portion of exhaust gases back into the engine intake, reducing combustion temperatures and thereby lowering NOx emissions.
1.3 Technological Advancements
Technological advancements in the late 20th and early 21st centuries saw improvements in EGR system efficiency and integration. Enhanced control units and valve designs optimized the balance between emissions reduction and engine performance.
As automotive technology progressed, EGR systems evolved from rudimentary designs to sophisticated components integral to modern emissions control strategies. Understanding this evolution is crucial for evaluating the effectiveness and necessity of contemporary EGR solutions.
Explore the operating principle of EGR systems and their impact on engine performance and emissions.

2. Operating Principle of EGR Systems
The operating principle of Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) systems revolves around controlling engine emissions by reintroducing exhaust gases into the combustion chamber. This process aims to reduce the formation of nitrogen oxides (NOx) during combustion.
2.1 Functionality of EGR Valves
The EGR valve regulates the flow of exhaust gases back into the intake manifold. It opens and closes based on engine load and operating conditions to maintain optimal combustion temperatures.
2.2 Mechanism of NOx Reduction
By recirculating exhaust gases, the EGR system lowers the oxygen concentration in the combustion chamber. This reduces peak combustion temperatures, inhibiting the formation of NOx compounds.
2.3 Integration with Engine Management Systems
Modern EGR systems are intricately linked with engine control units (ECUs) that monitor and adjust EGR operation in real-time. This integration ensures precise emissions control without compromising engine performance.
Understanding the operational dynamics of EGR systems illuminates their role in achieving regulatory compliance and enhancing environmental stewardship. Next, we'll delve into the specific differences in EGR implementation between gasoline and diesel engines.
Explore the nuances of EGR systems in gasoline versus diesel engines to highlight their distinct challenges and efficiencies.
3. Differences in EGR Implementation: Gasoline vs. Diesel Engines
The application of Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) systems varies significantly between gasoline and diesel engines due to their unique combustion characteristics and emission control requirements. Understanding these differences is essential for optimizing engine performance and emissions compliance.
3.1 EGR Systems in Gasoline Engines
3.1.1 Adaptability and Optimization
In gasoline engines, EGR systems face challenges related to variable engine loads and fuel-air ratios. Optimizing EGR flow rates and timing is critical to balancing emissions reduction with maintaining fuel efficiency and power output.
3.1.2 Impact on Combustion Efficiency
EGR in gasoline engines helps mitigate knock and pre-ignition tendencies by reducing peak combustion temperatures. This enhances fuel combustion stability and supports compliance with stringent emissions standards.
3.1.3 Technological Advancements
Recent advancements in gasoline engine EGR systems include variable valve timing and sophisticated ECU algorithms. These technologies enable finer control over EGR operation, enhancing overall engine efficiency and emissions performance.
Effective EGR implementation in gasoline engines underscores the importance of technological innovation and adaptive control strategies in achieving environmental objectives without compromising driving dynamics.
Explore the unique challenges and benefits of EGR systems in diesel engines, emphasizing their critical role in emissions control and operational efficiency.
4. Differences in EGR Implementation: Gasoline vs. Diesel Engines
Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) systems play distinct roles in gasoline and diesel engines, tailored to their combustion characteristics and emission reduction strategies. Understanding these differences is crucial for optimizing engine performance and meeting regulatory standards.
4.1 EGR Systems in Diesel Engines
High-Pressure Environment
Diesel engines operate under higher compression ratios than gasoline engines, resulting in elevated combustion temperatures and increased NOx formation. EGR systems in diesel engines are designed to mitigate these effects by lowering oxygen levels and temperature peaks in the combustion chamber.
EGR Valve Design and Function
EGR valves in diesel engines are robustly engineered to withstand high exhaust temperatures and pressures. They must maintain precise control over exhaust gas recirculation to balance emissions reduction with engine efficiency and reliability.
Integration with Turbocharging
Many modern diesel engines incorporate turbocharging for enhanced power and efficiency. EGR systems in these engines work in conjunction with turbochargers to optimize performance while meeting emissions targets.
The implementation of EGR systems in diesel engines highlights their critical role in reducing NOx emissions under challenging operating conditions. Effective integration of EGR with turbocharging technology underscores advancements in diesel engine efficiency and environmental sustainability.
Explore the benefits and drawbacks associated with EGR systems across different engine types, providing insights into their real-world implications and operational considerations.
5. Benefits and Drawbacks of EGR Systems
Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) systems offer significant environmental benefits by reducing nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions in internal combustion engines. However, their implementation also introduces certain trade-offs that impact engine performance and maintenance requirements.
5.1 Environmental Benefits of EGR Systems
NOx Emissions Reduction
EGR systems effectively lower NOx emissions by recirculating a portion of exhaust gases, which dilutes oxygen levels in the combustion chamber. This process mitigates the formation of harmful nitrogen oxides, contributing to cleaner air quality.
Compliance with Emissions Standards
Regulatory agencies worldwide mandate stringent limits on vehicle emissions. EGR systems help automakers meet these standards by integrating NOx reduction technologies into engine designs.
Long-Term Environmental Impact
Reducing NOx emissions through EGR systems helps mitigate smog formation and acid rain, thereby promoting environmental sustainability and public health.
5.2 Drawbacks of EGR Systems
Impact on Engine Efficiency
Introducing exhaust gases into the intake can reduce overall combustion efficiency, potentially affecting fuel economy and power output, especially under certain operating conditions.
Maintenance and Reliability Issues
EGR valves and associated components may suffer from carbon buildup and wear over time, necessitating periodic maintenance or replacement to ensure optimal engine performance.
Complexity and Cost
The integration of EGR systems adds complexity to engine design and manufacturing processes. Moreover, implementing advanced EGR technologies can increase vehicle production costs.
Balancing the environmental benefits of NOx reduction with the operational challenges and costs associated with EGR systems underscores the importance of continuous technological advancement and regulatory alignment in automotive engineering.
Explore common real-world problems associated with EGR systems, providing practical insights into troubleshooting and maintenance considerations for vehicle owners and technicians.

6. Real-World Problems with EGR Systems
While Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) systems play a crucial role in reducing emissions, they are susceptible to various real-world issues that can impact engine performance and reliability. Understanding these common problems is essential for effective maintenance and troubleshooting.
6.1 Common EGR System Failures
EGR Valve Malfunction
One of the primary issues encountered with EGR systems is valve malfunction. This can manifest as stuck open or closed valves, leading to improper exhaust gas recirculation and potential drivability issues such as rough idling or engine hesitation.
Carbon Buildup
Over time, carbon deposits can accumulate within the EGR system, particularly around the valve and intake manifold. This buildup restricts flow and impedes proper EGR operation, necessitating periodic cleaning or maintenance.
Sensor and Control Unit Issues
Faulty sensors or control units can disrupt EGR system operation by providing inaccurate data or failing to actuate the EGR valve as needed. This can trigger check engine lights (CEL) and impact overall engine performance.
6.2 Practical Maintenance Tips
Regular Inspection and Cleaning
Routine inspection and cleaning of EGR valves and associated components can prevent carbon buildup and ensure optimal system performance. Use recommended cleaning solutions and procedures to maintain efficiency.
Diagnostic Tools and Software
Utilize diagnostic tools and software to monitor EGR system parameters and identify potential issues early. This proactive approach aids in timely repairs and prevents costly engine damage or emissions non-compliance.
Consultation with Automotive Experts
For complex EGR system issues or persistent faults, seek guidance from qualified automotive technicians or engineers. Their expertise can provide tailored solutions and ensure proper maintenance practices are followed.
Navigating common EGR system challenges requires a proactive approach to maintenance and diagnostics. By addressing issues promptly and implementing preventive measures, vehicle owners can optimize engine performance and extend component longevity.
Discuss the implications of completely deleting the EGR system, addressing concerns and considerations for vehicle owners contemplating this modification.
7. Considerations for EGR System Deletion
The debate surrounding Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) system deletion revolves around potential performance gains versus legal and environmental considerations. Understanding the implications of egr delete kit is crucial for informed decision-making among vehicle owners and enthusiasts.
7.1 Implications of EGR System Deletion
Performance Enhancement
Removing the EGR system can potentially increase engine power and responsiveness by eliminating restrictions caused by exhaust gas recirculation. This modification is popular among performance enthusiasts seeking improved throttle response and acceleration.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance
In many regions, tampering with emissions control systems, including EGR deletion, is illegal and may result in fines or vehicle registration issues. Compliance with local emissions regulations should be carefully considered before pursuing EGR deletion.
Environmental Impact
EGR systems play a vital role in reducing nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions, contributing to cleaner air quality and environmental sustainability. Deleting the EGR system can reverse these benefits and increase a vehicle's environmental footprint.
7.2 Considerations for Vehicle Owners
Engine Longevity and Reliability
While EGR deletion may offer short-term performance gains, it can potentially affect long-term engine reliability and durability. Increased combustion temperatures and potential for engine knock may necessitate additional engine modifications or upgrades.
Alternative Solutions
Explore alternative solutions such as upgrading EGR components, installing performance-oriented EGR delete kits, or optimizing engine tuning to achieve a balance between emissions compliance and desired performance outcomes.
The decision to delete the EGR system involves weighing performance benefits against legal, environmental, and long-term reliability considerations. Vehicle owners should prioritize compliance with emissions regulations and consider sustainable alternatives to achieve desired performance enhancements.
Discuss operational tips and best practices for maintaining EGR systems or managing modifications effectively, providing practical guidance for vehicle owners and enthusiasts.
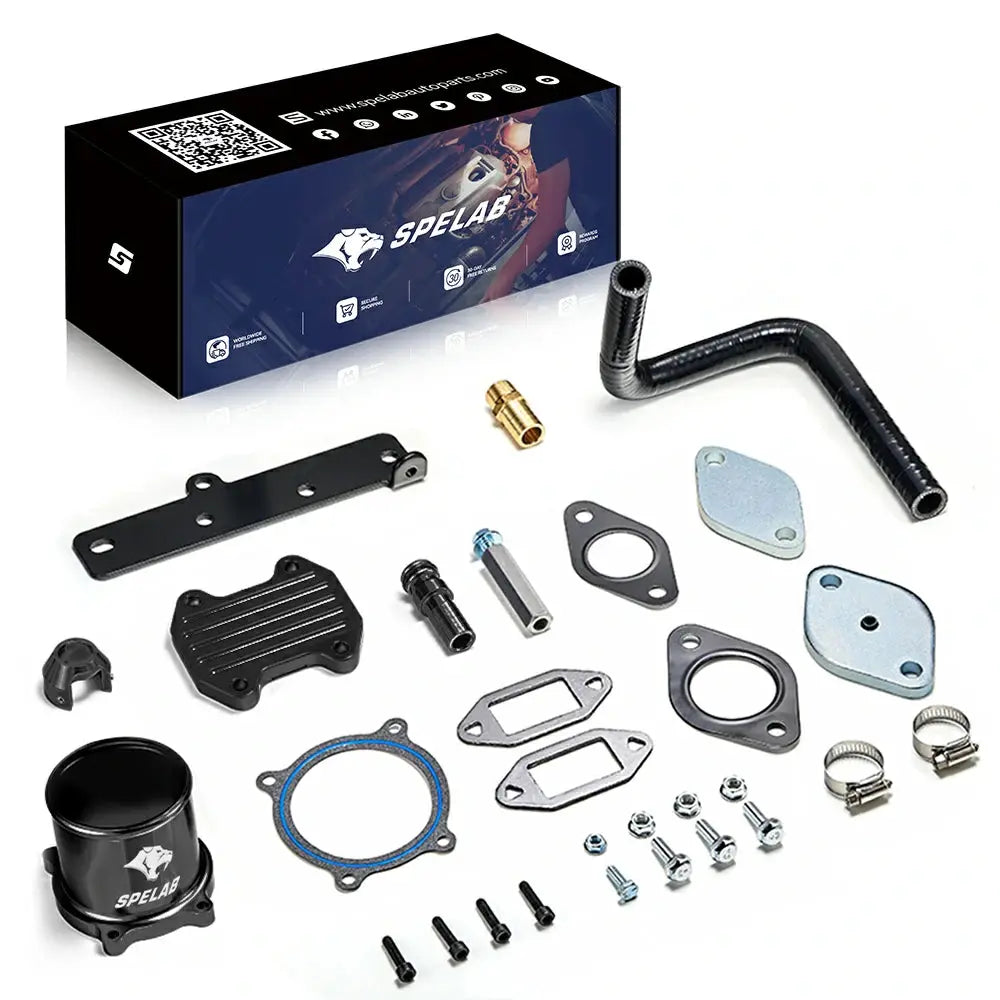

Fitment:
2013 Dodge Ram 2500 3500 6.7L Cummins Diesel
2014 Dodge Ram 2500 3500 6.7L Cummins Diesel
2015 Dodge Ram 2500 3500 6.7L Cummins Diesel
2016 Dodge Ram 2500 3500 6.7L Cummins Diesel
2017 Dodge Ram 2500 3500 6.7L Cummins Diesel
2018 Dodge Ram 2500 3500 6.7L Cummins Diesel
8. Operational Tips and Best Practices for EGR Systems
Effectively managing Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) systems involves proactive maintenance and adherence to best practices. Implementing these strategies ensures optimal performance, reliability, and compliance with emissions regulations.
8.1 Maintenance and Care for EGR Systems
8.1 Regular Inspection and Cleaning Schedule routine inspections of EGR valves, tubes, and associated components for signs of wear or carbon buildup. Clean or replace components as necessary to maintain proper functionality and prevent performance degradation.
Use of High-Quality Components
Opt for OEM or high-quality aftermarket EGR components and replacement parts. Quality components ensure durability and reliability, minimizing the risk of premature failure or malfunction.
Engine Oil and Filter Maintenance
Maintain regular oil changes using manufacturer-recommended oil and filters. Clean engine oil helps prevent carbon and sludge buildup in the EGR system, preserving overall engine performance and efficiency.
8.2 Optimization Strategies
Engine Tuning and Calibration
Consider professional engine tuning and calibration to optimize EGR system performance. Tuning adjustments can enhance fuel efficiency, reduce emissions, and improve overall engine responsiveness.
Monitoring System Parameters
Utilize diagnostic tools to monitor EGR system parameters and performance metrics regularly. Identify potential issues early and take corrective actions to prevent costly repairs or emissions non-compliance.
Educate and Train Personnel
For fleet operators or automotive technicians, provide training on EGR system operation, maintenance procedures, and troubleshooting techniques. Empowered personnel can effectively manage EGR systems and ensure fleet reliability.
Adhering to best practices for EGR system maintenance and optimization enhances vehicle reliability, performance, and compliance with emissions regulations. By prioritizing proactive care and quality components, vehicle owners and operators can extend the lifespan of EGR systems and maximize operational efficiency.
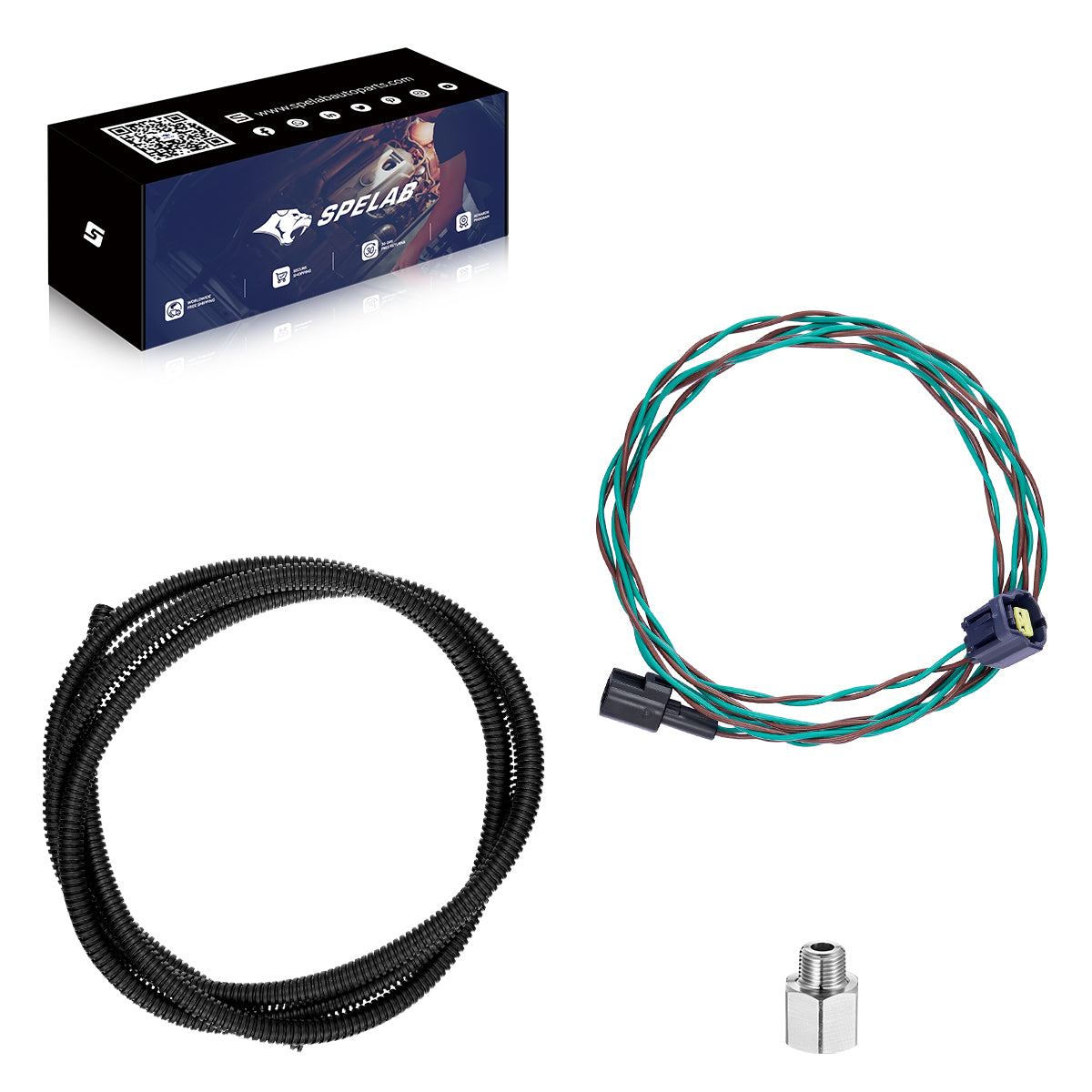

Package Includes: EGT Sensor Harness Wiring Harness Protector Sensor Threaded Fitting for Exhaust Flap
Buy NowFAQs
Q1: What does a full EGR delete do?
A1: A full EGR delete removes the entire exhaust gas recirculation system from the vehicle, including the EGR valve and associated components. This modification aims to improve engine performance by eliminating exhaust gas restrictions.
Q2: Is EGR delete bad for the engine?
A2: While an EGR delete can increase horsepower and throttle response, it may lead to higher nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions, potentially impacting environmental compliance and engine longevity.
Q3: Can I just delete my EGR?
A3: Deleting the EGR system is possible, but it's important to consider legal implications and environmental consequences. Check local regulations before proceeding with any modifications.
Q4: Will an engine run without an EGR valve?
A4: Yes, an engine can run without an EGR valve. However, its operation may result in increased emissions and potential non-compliance with emissions standards in some regions.
Q5: What happens if I unplug the EGR?
A5: Unplugging the EGR valve disrupts exhaust gas recirculation, potentially triggering a check engine light (CEL) and affecting engine performance. It's not recommended without proper modifications.
Q6: Is an EGR delete illegal?
A6: In many jurisdictions, modifying or deleting emissions control systems like the EGR is illegal if it leads to increased emissions beyond permissible limits. Always check local laws and regulations.
Q7: How does an EGR affect fuel economy?
A7: EGR systems can slightly reduce fuel economy by altering combustion dynamics and engine efficiency. The impact varies based on driving conditions and engine design.
Q8: What are the signs of a failing EGR valve?
A8: Common signs include rough idling, engine hesitation, increased emissions, and illuminated check engine lights (CEL). These symptoms may indicate EGR valve or system malfunction.
Q9: Can you clean an EGR valve?
A9: Yes, EGR valves can be cleaned to remove carbon deposits and restore proper operation. Use manufacturer-recommended cleaning solutions and follow specific procedures for best results.
Q10: How often should EGR valves be replaced?
A10: EGR valve replacement intervals vary based on vehicle usage and manufacturer recommendations. Generally, they may need replacement every 50,000 to 100,000 miles or earlier if symptoms of failure arise.






2 comments
No gaskets or bolts for Lbz ybridge,,,why
No gaskets or bolts for Lbz ybridge,,,why